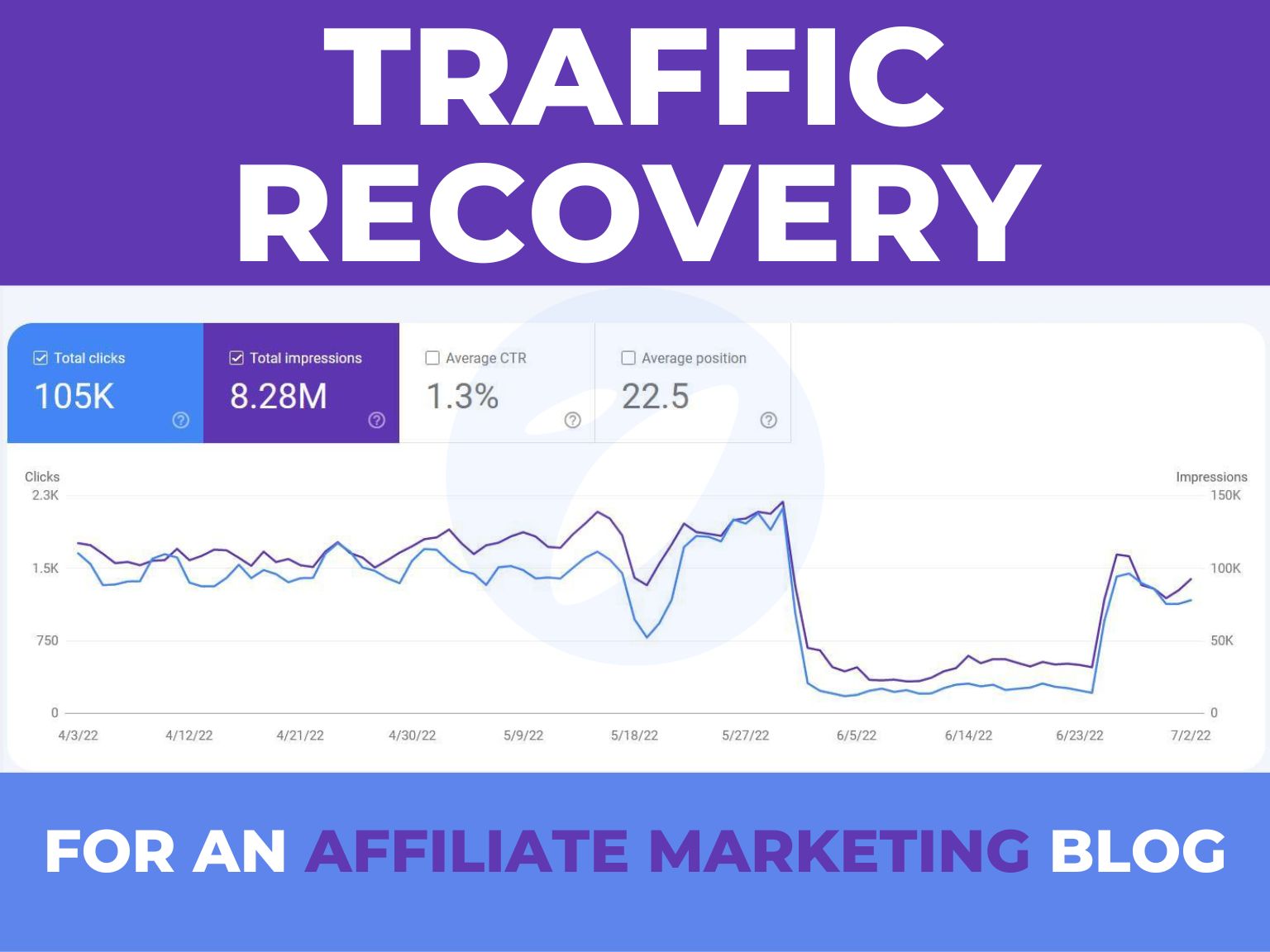
Introduction to Effective Keyword Research
Keywords form the cornerstone of SEO. Their effective research and application can significantly enhance the visibility and ranking of your content on search engines. This detailed guide aims to demystify the keyword research process, offering insights, practical examples, and tips for mastering this crucial aspect of SEO.
Understanding the Importance of Keywords in SEO:
-
Driving Traffic: Proper keyword research ensures that your content aligns with what your target audience is searching for, thereby increasing organic traffic.
-
Understanding User Intent: By researching keywords, you gain insights into what your potential customers are looking for and their intentions, which can guide your content strategy.
-
Competitive Edge: Effective keyword research can give you a leg up on competitors by identifying niche or less competitive keywords that they might have overlooked.
The Evolution of Keyword Research:
-
Historical Perspective: In the early days of SEO, keyword research was simplistic, focusing mainly on high-volume search terms. However, with search engines becoming more sophisticated, the approach has evolved.
-
Current Trends: Today, keyword research encompasses understanding search intent, long-tail keywords, and semantic search relevance, moving beyond mere search volume and competition data.
Understanding Your Audience
To effectively research keywords, you first need to understand who your audience is and what they are searching for. This understanding forms the foundation of your SEO strategy.
Identifying Your Target Audience:
-
Demographics: Consider age, location, gender, interests, and income level. For instance, a website selling sports equipment would target a different demographic than one offering retirement planning advice.
-
Psychographics: Understanding the lifestyle, values, and attitudes of your audience can further refine your keyword research.
Analyzing Search Intent:
-
Navigational: Users looking for a specific website or page.
-
Informational: Searches conducted to find information on a topic.
-
Transactional: Searches where the user intends to make a purchase or engage in another specific online activity.
Real-Time Examples:
-
E-commerce Store: An online clothing retailer might focus on transactional keywords like “buy men’s winter jackets online”.
-
Blog: A travel blog might target informational keywords such as “best destinations in Europe”.
Tools for Keyword Research
Being an SEO Specialist, it’s essential to find the right keywords with the correct search intent and demand. Keyword research tools save countless hours finding the right keywords for any SEO campaign. They range from basic free tools to advanced paid services, each offering unique features.
Overview of Popular Tools:
-
Google Keyword Planner: A free tool that provides data on search volume and competition, ideal for beginners.
-
Ahrefs: Offers advanced features like keyword difficulty score and SERP analysis, suitable for more in-depth research.
-
SEMrush: Known for its comprehensive keyword data and competitive analysis features.
Key Features to Look For:
-
Search Volume Data: Helps determine how often a keyword is searched.
-
Keyword Difficulty Score: Indicates how hard it is to rank for a particular keyword.
-
Related Keywords Suggestions: Provides ideas for other relevant keywords.
Example of Tool Usage:
-
Case Study of a Local Bakery: Using Ahrefs, the bakery identifies high-volume, low-competition keywords like “gluten-free bakery in [City Name]” and integrates them into their website content and blog posts.
Types of Keywords
Understanding different types of keywords is crucial for crafting an effective SEO strategy. Each type serves a specific purpose in attracting the right audience to your website.
Short-tail vs. Long-tail Keywords:
-
Short-tail Keywords: These are broad, general keywords, often comprising one or two words. For example, “coffee” or “digital cameras.” While they have a high search volume, they also face stiff competition and may not attract highly targeted traffic.
-
Long-tail Keywords: These are more specific and often longer phrases that are closer to what users are searching for. For instance, “organic fair trade coffee beans” or “best digital cameras under $500.” They typically have lower search volumes but attract more targeted, often conversion-ready traffic.
Branded vs. Non-Branded Keywords:
-
Branded Keywords: These include the brand name or specific product names. For example, “Nike running shoes” or “Apple iPhone 12.” They are crucial for businesses looking to capture traffic specifically interested in their brand or products.
-
Non-Branded Keywords: These are general terms related to an industry or product category but without brand names. For example, “running shoes” or “smartphones.” They are essential for attracting a broader audience who might not be aware of your brand.
Real-time Examples and Case Studies:
-
E-commerce Example: An online electronics retailer might use short-tail keywords like “laptops” for broader reach, while employing long-tail keywords like “gaming laptops with VR support” for targeted traffic.
-
Service Industry Example: A local plumbing business might use branded keywords like “Ace Plumbing Services” while also targeting non-branded keywords like “emergency plumbing repair.”
Finding the Right Keywords
Selecting the right keywords is a critical step in your SEO journey. It involves understanding not just what people are searching for, but also the competition and potential traffic each keyword can bring.
Brainstorming Techniques:
-
List Down Core Topics: Start by listing down the core topics relevant to your business or industry. For a fitness blog, these might include “workout routines,” “nutrition tips,” and “fitness equipment.”
-
Use Tools for Idea Generation: Leverage tools like AnswerThePublic or Google’s “People also ask” section to find commonly asked questions and topics in your field.
Competitor Analysis:
-
Study Competitors’ Keywords: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to see what keywords your competitors are ranking for. This can provide insights into potential keywords you might have overlooked.
-
Analyze Their Content and Strategy: Look at the type of content your competitors are creating. Are they focusing on blog posts, tutorials, product reviews? This can inform the kind of content you should create.
Real-time Examples and Case Studies:
-
Blogging Example: A food blogger might find that competitors are ranking for “easy vegan recipes,” prompting them to create content around this keyword with their unique twist.
-
Retail Example: An online clothing retailer notices competitors are ranking for “affordable summer dresses” and decides to create a marketing campaign around their range of summer dresses.
Evaluating Keyword Difficulty
Identifying the level of difficulty to rank for a particular keyword is essential. It helps in prioritizing efforts towards keywords that are attainable and most beneficial for your SEO strategy.
Understanding Competition:
-
High-Competition Keywords: These are often short-tail keywords with high search volumes. Ranking for these requires significant SEO effort and high-quality content.
-
Low-Competition Keywords: These are often long-tail keywords or very specific phrases. They are easier to rank for and can be ideal for new websites or niche markets.
Tools for Difficulty Analysis:
-
Use of Keyword Difficulty Tools: Tools like Moz’s Keyword Explorer or Ahrefs provide a keyword difficulty score, helping you gauge how hard it will be to rank for a specific keyword.
-
Analyzing SERPs: Manually checking the search engine results pages (SERPs) for a keyword gives insights into who your competitors are and the quality of content you need to produce to rank.
Case Studies on Difficulty Analysis:
-
Case Study 1: A small travel blog successfully targets low-competition keywords like “offbeat destinations in Italy” rather than competing with big players for “Italy travel guide.”
-
Case Study 2: A tech startup focuses on niche long-tail keywords like “affordable CRM software for small businesses” to rank higher and quicker than going for broader terms like “CRM software.”
Keyword Relevance and Context
Choosing keywords that are relevant to your content and contextually appropriate is essential. It’s not just about what people are searching for, but also ensuring your content genuinely addresses those queries.
Matching User Intent:
-
Understanding User Intent: This involves categorizing keywords based on the user’s goal, be it informational, navigational, or transactional.
-
Aligning Content with Keywords: Ensure your content matches the intent behind the keywords. For instance, if the keyword is “how to bake a chocolate cake,” the content should provide a step-by-step recipe, not just a history of chocolate cakes.
Contextual Relevance:
-
Beyond Exact Matches: Search engines now understand context, so it’s crucial to use keywords in a way that fits naturally into your content.
-
Topic Clusters: Creating clusters of content around a specific topic, using a variety of related keywords, can boost your overall relevance and authority on a subject.
Success Stories:
-
Blogging Success: A health and wellness blog increases its traffic by creating content clusters around “yoga for beginners,” covering various aspects like poses, benefits, and equipment.
-
Retail Success: An online fashion retailer revamps its product descriptions and blog posts to include contextually relevant keywords, significantly improving its search engine rankings.
SEO Writing Tips
Crafting SEO-friendly content involves more than just sprinkling keywords throughout your text. It’s about integrating them seamlessly while keeping the writing engaging and informative.
Writing with Keywords:
-
Natural Integration: Use keywords in a way that sounds natural within your content. Forced or awkward usage can detract from the reader’s experience.
-
Using Variants and Synonyms: This helps in catering to different search queries and improves the overall readability of the content.
Maintaining Keyword Density:
-
Ideal Density: Aim for a keyword density of 1-2%. This means using your primary keyword once or twice for every 100 words.
-
Avoiding Overstuffing: Excessive use of keywords can lead to penalties from search engines and a poor user experience.
Best Practices Examples:
-
Blog Example: A travel blog writes an article titled “10 Best Beaches in California,” using the primary keyword naturally throughout the content and in subheadings.
-
E-commerce Example: An electronics web store incorporates keywords into product descriptions and titles without compromising on the clarity and descriptiveness of the text.
Local SEO and Keywords
For businesses targeting a local audience, incorporating local SEO tactics into their keyword strategy is crucial.
Importance of Localized Keywords:
-
Targeting Local Searches: Localized keywords, like “coffee shop in downtown Boston,” help in capturing the audience looking for specific services in a particular area.
-
Inclusion in Local Listings: Being present in local directories and listings with the right keywords can significantly boost visibility.
Strategies for Local SEO:
-
Optimizing Google My Business: Ensure your Google My Business listing is complete and optimized with local keywords.
-
Local Content Creation: Create content relevant to your local area, such as local event guides or news, and use local keywords.
Case Studies:
-
Restaurant Success: A restaurant in Seattle optimizes its website with keywords like “best seafood restaurant in Seattle,” seeing a substantial increase in local foot traffic.
-
Service Provider Success: A plumbing service in Austin creates a series of blog posts about common plumbing issues in Austin, using local keywords, and climbs up the local search rankings.
Tracking and Adjusting Your Strategy
Constantly monitoring and adjusting your keyword strategy is vital to maintaining and improving your SEO performance.
Methods to Monitor Keyword Performance:
-
Use Analytics Tools: Tools like Google Analytics and Ahrefs provide insights into how your keywords are performing in terms of traffic and rankings.
-
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your keyword performance to identify trends, successes, and areas for improvement.
Real-time Strategy Adjustment:
-
Adapt to Trends: Be agile in adapting your strategy to current trends. For instance, if a new product becomes popular in your industry, consider incorporating related keywords.
-
Respond to Performance Data: If certain keywords are underperforming, research why and adjust your strategy. Maybe the keyword is too competitive, or your content doesn’t match user intent well.
Case Studies:
-
E-commerce Adjustment: An online bookstore finds that “audiobooks for children” is performing well, so they increase their content and inventory in this category.
-
Blog Strategy Shift: A technology blog notices a shift in interest towards “sustainable tech” and starts focusing more content in this area, gaining increased traffic.
Avoiding Keyword Stuffing
While keywords are essential, their overuse, known as keyword stuffing, can harm your SEO efforts.
Recognizing and Avoiding Overuse:
-
Be Mindful of Density: Keep track of your keyword density to ensure it remains within the ideal range (1-2%).
-
Readability First: Always prioritize the natural flow and readability of your content. If a keyword feels forced, it probably shouldn’t be there.
The Risks of Overstuffing:
-
Search Engine Penalties: Search engines can penalize your site for keyword stuffing, leading to lower rankings.
-
Poor User Experience: Overstuffed content is often difficult to read and can drive away potential customers.
Examples of Overuse:
-
Negative Example: A website about pet care repeatedly uses “best pet food” in every sentence, making the content unreadable and unhelpful.
-
Positive Adjustment: The same website then revises the content, using the keyword naturally and focusing on providing valuable information, resulting in better user engagement.
Long-term Keyword Strategy
Developing a long-term keyword strategy involves anticipating future trends and staying adaptable to algorithm changes.
Planning for Future Trends:
-
Stay Informed: Keep up with industry news and trends to anticipate future popular keywords.
-
Use Predictive Tools: Some advanced SEO tools offer predictive insights based on trending data and search patterns.
Adapting to Algorithm Changes:
-
Understand SEO Updates: Regularly update your knowledge about search engine algorithm changes and how they might affect keyword ranking.
-
Flexibility in Strategy: Be prepared to adjust your keyword strategy in response to these changes, ensuring your SEO remains effective.
Guide for Future Planning:
-
Anticipating Market Changes: A tech company stays ahead by researching and incorporating upcoming tech trends into their content strategy.
-
Algorithm Update Response: A lifestyle blog quickly adapts to a new Google algorithm that prioritizes user experience, restructuring their content to be more engaging and interactive.
Integrating Keywords in Technical SEO
Effective keyword integration extends beyond content and into the technical aspects of SEO, playing a critical role in enhancing your website’s visibility and search engine friendliness.
Optimizing Meta Tags and Descriptions with Keywords:
-
Meta Titles and Descriptions: Ensure your primary keywords are included in the meta titles and descriptions. This not only helps with ranking but also encourages users to click on your website in search results.
-
Header Tags: Use keywords in H1, H2, and H3 tags to structure your content effectively and make it easier for search engines to understand the hierarchy and relevance of your content.
URL Structures: Best Practices:
-
Descriptive URLs: Create URLs that are descriptive and include your primary keywords. For example, use /best-organic-dog-food instead of /product12345.
-
Simplicity and Readability: Keep URLs simple, readable, and free of unnecessary parameters or numbers.
Real-time Examples and Case Studies:
-
E-commerce Optimization: An online fashion retailer uses descriptive URLs like /women-summer-dresses for product pages, resulting in better search engine indexing and user understanding.
-
Blog Post Enhancement: A fitness blog optimizes its posts with keyword-rich titles and meta descriptions, leading to increased click-through rates from search engine results pages.
Advanced Keyword Research Techniques
To stay ahead in the competitive SEO landscape, utilizing advanced keyword research techniques can provide a deeper understanding of search trends and user behavior.
Exploring Semantic Search and LSI Keywords:
-
Semantic Search Relevance: Understand the context in which keywords are used and how search engines interpret these contexts. This involves looking at synonyms and related phrases.
-
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: These are keywords semantically related to your primary keyword. Including them helps search engines understand the content better and can improve rankings.
Techniques for a Deeper Insight:
-
Competitor Keyword Gap Analysis: Use tools to identify keywords your competitors are ranking for, which you are not.
-
Searcher’s Journey Analysis: Understand the path your audience takes from initial awareness to the final decision-making process, and use it to target keywords at different stages.
Case Studies and Application:
-
Travel Website’s Semantic Strategy: A travel website incorporates terms like “affordable holiday destinations” and “budget travel tips” alongside its primary keyword “cheap travel,” enhancing its relevance.
-
Health Blog’s Journey Analysis: A health and wellness blog targets keywords like “beginner yoga tips” and “advanced yoga poses,” catering to audiences at different stages of their yoga journey.
Conclusion
Effective keyword research is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires continuous learning, experimentation, and adaptation. By understanding and applying the principles and techniques discussed in this guide, you can significantly improve your website’s SEO performance and online visibility.
Recap of Key Points:
-
Understand the importance of keyword research and its role in SEO.
-
Use a variety of tools and techniques for comprehensive keyword discovery and analysis.
-
Integrate keywords thoughtfully in content and technical SEO elements.
Motivation for Continuous Learning:
-
SEO is an ever-evolving field, with search algorithms and user behaviors constantly changing. Staying informed and adaptable is crucial for long-term success.
-
Experiment with new strategies, track your results, and be ready to pivot your approach as needed.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between short-tail and long-tail keywords?
-
Short-tail Keywords: These are typically broad, one-to-two-word phrases with high search volume but also high competition. Example: “coffee”.
-
Long-tail Keywords: These phrases are longer, more specific, and usually consist of three or more words. They have a lower search volume but are less competitive and often yield higher conversion rates. Example: “organic fair trade coffee beans”.
-
-
How often should I review and adjust my keyword strategy?
-
Review and adjust your keyword strategy at least quarterly. However, staying alert to major industry trends or changes in search engine algorithms may necessitate more frequent adjustments.
-
-
What are LSI keywords, and why are they important?
-
LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords are terms and phrases that are semantically related to your primary keyword. They help search engines understand the context of your content, improving its relevance and potentially its rankings. Example: For the primary keyword “digital marketing,” LSI keywords could include “online advertising,” “SEO,” and “content marketing.”
-
-
Can keyword research tools help predict future trends?
-
Yes, many advanced keyword research tools offer trend analysis features that can help predict future search trends. By analyzing search volume patterns and related keywords, these tools can provide insights into emerging topics and interests.
-
-
How do I balance keyword density without overstuffing?
-
Aim for a keyword density of 1-2%. Use keywords naturally within the content. Read your content aloud to ensure it sounds conversational and not forced. Remember, the primary goal is to provide value to your readers, not just to insert keywords.
-
-
What role do keywords play in local SEO?
-
In local SEO, keywords are used to target specific geographic locations. These are crucial for businesses looking to attract customers in their vicinity. Example: “best coffee shop in downtown Portland”.
-
-
How can I identify my audience’s search intent?
-
Analyze the types of queries that lead users to your site using tools like Google Analytics. Look at the content of your pages that rank well to understand what users expect. Engage with your audience through surveys or social media to gather direct insights.
-
-
Are there any risks associated with keyword stuffing?
-
Yes, keyword stuffing can lead to penalties from search engines, resulting in lower rankings. It also degrades the user experience, as content often becomes unreadable or irrelevant.
-
-
How does keyword research integrate with technical SEO?
-
Keyword research informs technical SEO by identifying the best terms to include in meta tags, descriptions, and URLs, enhancing a site’s visibility and relevance in search engine results.
-
-
What are some advanced keyword research techniques?
-
Advanced techniques include:
-
Competitor Keyword Gap Analysis: Identifying keywords your competitors rank for that you don’t.
-
SERP Analysis: Studying search engine results pages to understand what type of content ranks for your targeted keywords.
-
Seasonal Trend Analysis: Adjusting your keyword strategy based on seasonal trends and events.
-
-